Basic Understanding of Answer Engines and Their Limitations
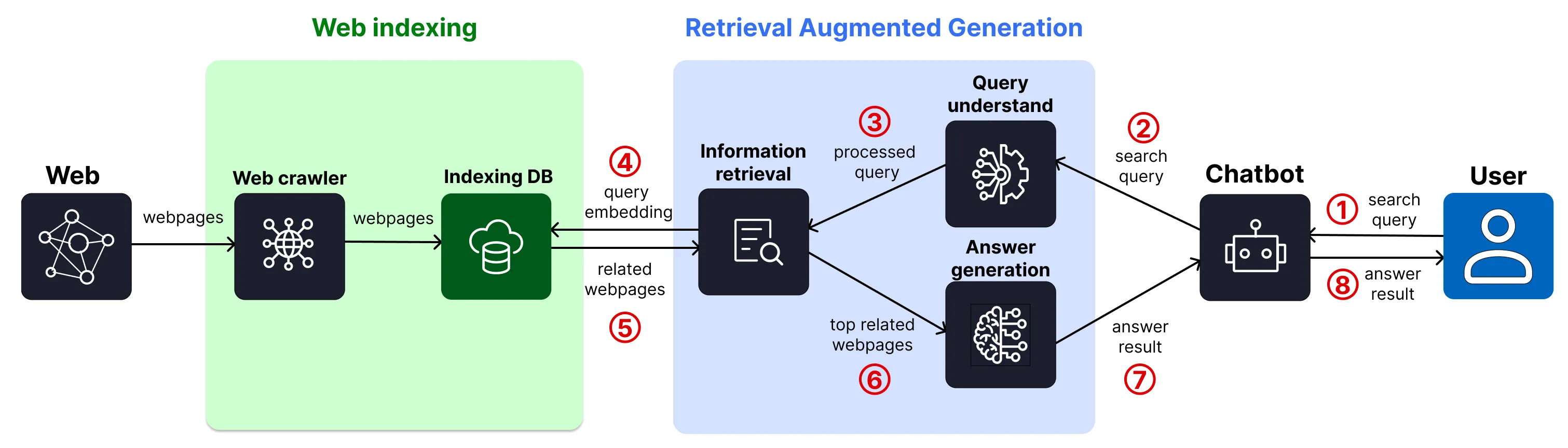
Figure 1. Simplified diagram of how an answer engine works
Answer engines such as Perplexity, Google Gemini, ChatGPT and more are changing the way people acquire information from the web. Instead of manually search, click, read, and summarize information from multiple sources by themselves, answer engines did all of these steps and provide content consumers a summary with inline references that is relevant to their search queries. However, there are some intrinsic limitations to answer engines that are important to understand. But first, let’s understand how an answer engine works.
How does an answer engine work?
Answer engine comprises of two separated stages: web indexing and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). Figure 1 shows a simplified diagram of how an answer engine works.
Web indexing
Popular answer engines either build their own web index database or integrate with existing search engines’ index.
- Perplexity primarily relies on its own index for search results. 2
- Google Gemini utilizes the Google web index to provide search results. 1
- OpenAI ChatGPT integrates Bing’s index for its search capabilities. 3
- Anthropic’s Claude chatbot appears to use Brave’s index or potentially its own index. 4
- Microsoft Copilot leverages Bing’s index for its search functionalities 6 .
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
- Query understanding: This step involves multiple components, including natural language processing (NLP) to interpret the user’s intent, keyword analysis to identify relevant topics, and contextual understanding to ensure accurate results.
- Content retrieval: To answer a user query, the answer engine finds and ranks indexed webpages based on their content’s similarity to the user query, as well as other factors like page authority and domain authority. This ensures that the most relevant and trustworthy information is presented to the user.
- Answer generation: Once the most relevant sources are identified, the answer engine synthesizes the information into a concise, helpful response. This may include summarizing multiple pages, highlighting key facts, and presenting the answer in a conversational or structured format. Advanced engines may even cite their sources or provide interactive follow-ups.
The above describes the basic processing steps of an answer engine. Some answer engines provide features such as Pro Search or Deep Research that add more processing steps, including query deeper understanding, reasoning, and evaluation of answer results to provide a better final answer result.
Limitations of answer engines
As observed in the real world cases across multiple domains such as legal, healthcare, and more, answer engines can still provide answers that have missing information, bias, and hallucinated information. This is due to the limitations of the processing steps in the web indexing and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) stages. Below, we discuss the main limitations.
- Missing information: Different answer engines have different indexing latency. If the content was updated but had not been crawled and indexed, the information will not be included in the answer results.
- Bias information: Answer engines rank the relevancy of indexed webpages to a user query differently using different algorithms and metrics. As a result, the final answer results maybe bias to the retrieved webpages.
- Hallucinated information: Answer engines rely on large language models (LLMs) to generate answers from the retrieved content. One of the limitations of LLMs is hallucination, where the model generates inaccurate information. Therefore, answer engines can provide answers that are not accurate, especially when the retrieved content is not relevant to the user query.
In the age of information overload, people are relying on answer engines to provide them with accurate and relevant answers to their queries. However, one should be aware of the limitations of these engines. Simple actions to mitigate the limitations are:
- Check the trustworthiness and relevancy of the referenced content used by answer engines. For example, check the author and date of the referenced content.
- Ask follow-up questions to the answer engine to get more information.
- Use multiple answer engines to get a more comprehensive answer.
References
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4 Anthropic appears to be using Brave to power web searches for its Claude chatbot by TechCrunch (March2025)
- 5
- 6
